Ranks
Ranks in the Corporate Hierarchy feature represent the different levels that may exist in your organization. Each rank can have different permissions and be responsible for subordinate ranks.
The default rank is Global. It is the highest rank in the Corporate Hierarchy and can configure all ranks that are added below it.
When you add ranks, be aware that users assigned to a rank can only edit other ranks that are subordinate in the Corporate Hierarchy. Any ranks that are above or parallel will not be accessible.
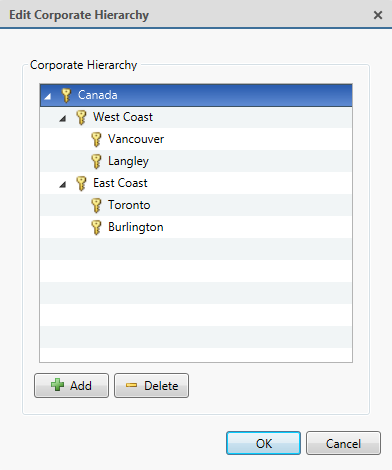
The following image is an example of a Corporate Hierarchy with multiple ranks. Canada is the highest, Global rank. West Coast and East Coast are of equal rank to each other, and one rank below Canada. Users belonging to East Coast cannot edit ranks below West Coast and vice versa.
Unranked Groups
The Unranked groups are above the Corporate Hierarchy and cannot be deleted or edited.
Users belonging to Unranked groups are able to create and edit any ranked or Unranked groups and users if they have the Setup user and group settings privilege.
The default groups Administrators, Power Users, Restricted Users, and Standard Users are Unranked.
Deleted Ranks
If a rank is deleted, groups in this rank are removed from the hierarchy and assigned an orphaned rank. An orphaned rank is the lowest rank possible and is only visible to Unranked and Global users.
Unranked and Global users can reassign group ranks at any time. Members of the orphaned rank have no Setup user and group settings privileges but still retain other privileges, e.g. viewing live video.
Deleting a rank will also delete all the ranks below it in the Corporate Hierarchy. Remotely synchronized users and groups may become inaccessible.
Ranked Site Families
Ranks can also be applied to sites that have been organized into families. Once a site has been assigned a rank, all groups, users and device access are subject to the site's rank in the hierarchy.
The Corporate Hierarchy is configured through the parent site and the Global rank is associated with the parent site. For more information, see Connecting Site Families.
Avigilon Control Center 6.6 | 20170922